“How to be first on Google” is my SEO guide for positioning on search engines . Here you will find all the SEO tricks and techniques to improve your ranking on Google!
What are we talking about
- 1 Being first on Google: why is it important?
- 2 What is SEO and why you can’t do without it
- 3 Enter the site in search engines
- 4 The SEO Guide: SEO tips and techniques on site
- 4.1 Optimization of the structure: the silo
- 4.2 The choice of keywords
- 4.3 URL Optimization
- 4.4 Title Optimization
- 4.5 Meta description optimization
- 4.6 Text optimization
- 4.7 Link Optimization
- 4.8 Image Optimization
- 4.9 Optimization of multimedia contents
- 4.10 HTTPS: Safe Browsing
- 4.11 Structured data
- 5 The SEO Guide: off-site techniques
- 6 SEO Tool
Being first on Google: why is it important?
Being on the first page of Google is essential for the success of a site: as revealed by a study by the highly influential Moz portal, 71.33% of clicks are made on the results of the first page . The second and third pages collect only 5.59% of clicks.
On the first page of Google, in particular, the first 5 results collect 67.60% of clicks and the results from sixth to tenth position collect only 3.73%.
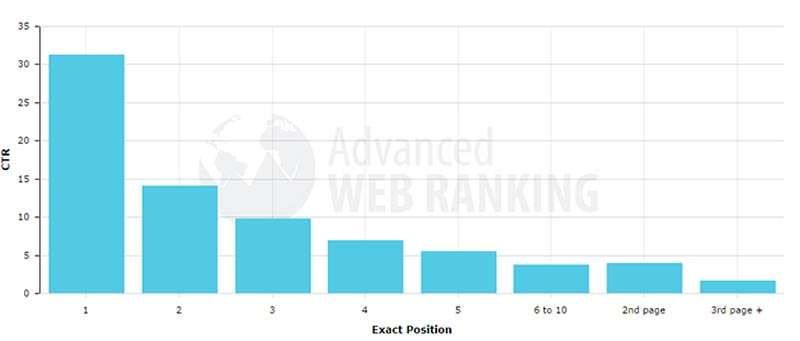
Obviously, if we always talk about Google and not the other search engines, there is a reason: Big G, alone, drives over 90% of world web traffic! Nice numbers, nothing to say… 🙂
What is SEO and why you can’t do without it
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization , or search engine optimization . It includes all those techniques to make your content more appealing to Google and “members” and improve the visibility of your site.
SEO techniques are divided into two broad categories: on site SEO techniques and off site SEO techniques. The former include: optimization of the HTML code , URLs, title, description, texts, images, multimedia content, links, creation of the sitemap.
Off-site SEO , on the other hand, aims at promoting the site and its contents through link earning and link building activities .
Enter the site in search engines
The indexing of websites is an automatic procedure . As soon as your site is created, search engines automatically detect it. The process isn’t instant – it can take hours or days. To shorten the time, there are procedures for submitting a site to search engines .
How to make your site appear on Google? You can use the page for adding and removing URLs . Reporting the site is simple: just enter the full URL (including, that is, the http: // or https: // prefix). You can also add comments or keywords to “explain” the page content.
How to submit a site to Bing? The procedure is just as simple: just go to the Submit your site to Bing page , enter the url and you’re done!
In general, to favor indexing on search engines it is advisable to create a sitemap , a site map . It is a document that describes the structure of a website . If you are an expert, you can create it by hand, use an online service such as Xml Sitemap Generator or, if your site was created with WordPress , use a plugin .
The SEO Guide: on site SEO tricks and techniques
Optimization of the structure: the silo
How to rank on Google? The starting point can only be the organization of the site’s contents in a coherent , clear structure that is easy for the user to navigate. The ideal structure, in this sense, is the so-called “silo structure” . It is a division of contents similar to that of a book: the information is divided into main semantic areas (the “silo pages” ) similar to the chapters of a book and further divided into smaller containers (to continue the metaphor of the book, paragraphs and subsections).
The silo structure was first spotted by Bruce Clay, who talks about it extensively on his website . Here is a visual example:
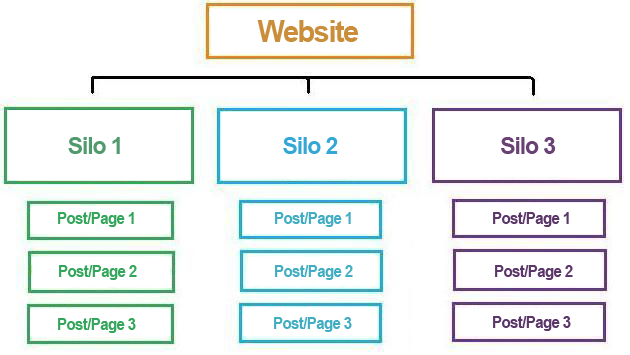
How is the silo structure built with WordPress? Simple. The “silo pages” are created as “parent” pages ; the next level can be represented by “child” pages . I did this for my site; for example: https://wpradar.com/website-creation/ is a “parent” page and https://wpradar.com/website-creation/aziendali/ its “child” page . The alternative is to implement the classic category-post mechanism : in this way, the silo page is the archive page of a category (generated, therefore, dynamically) and the content placed at the level immediately below an article .
The choice of keywords
Do you know what the first SEO commandment is?
Treat every single piece of content as the answer to a specific need.
What does it mean? It means specializing, identifying your niche and occupying it . Search engines are seething with content: soaring is a matter of competence and specificity. Each content on your site must answer a query, or a “question” from users.
This is where keywords come into play. Keywords are those expressions that identify activities, sectors, objects, etc. for which you want to place a site on search engines. It is important to create the contents of a web page starting from a main keyword , exploring all the possible branches that make up a coherent semantic area. For example, for this article I worked on “how to be first on Google” (a keyphrase , rather than a keyword), developing all the concepts associated with the ranking theme.
Therefore, once the main topic of a page has been established, here are the criteria you must take into consideration when choosing keywords:
- The volume of traffic , or the average of monthly searches for that keyword
- Competition or competition , i.e. how many websites have already been indexed for that word. It is an important parameter, because it can affect the ease / difficulty of positioning (therefore on times and costs);
- Research intentions. The more specific the keyword is, the more likely it is that the purpose of that search is an action that is relevant to us, that is, a conversion (purchase, registration, etc.). For example, if I am looking for a “wedding photographer in Milan”, it is very likely that I am looking for a professional who can take the photos for my wedding. If I’m looking for “wedding photos”, maybe I just want to admire some beautiful shots!
The first two data are objectively measurable through Google AdWords Keyword Planner (edit: no more, unfortunately!), SeoZoom or Semrush , very powerful tools (for a fee) that analyze traffic flows and allow you to find new keywords . In fact, if it is appropriate to think starting from a main keyword, it is also advisable to create a long queue of keywords , very useful for intercepting the right target and stimulating clicks and conversions (purchases, subscriptions, etc.). To learn more, take a look at my guide on long tail keywords!
URL optimization
The URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a sequence of characters that locates a resource (page, document, image, etc.) on the internet. The address of a page (and the domain of the site) are essential elements to get first on Google.
The ideal is to create talking addresses , that is, discursive URLs that summarize the content of the page through keywords.
In general, the correct structure of an SEO friendly url is your sitename / keyword . Normally, conjunctions and prepositions, i.e. stop words , should not appear in urls. I advise you, however, to evaluate case by case : sometimes deleting a stop word can make the url less legible and alter its meaning; others, the presence or absence of stop words may lead to variations in search volumes (eg. “first on google” is more sought after than “first google”, which means nothing) and therefore a url with stop might be appropriate words. (To learn more about stop word, read the section below!)
Title optimization
By title we mean the




